6.7 KiB
rodo
rodo is a list-management tool for people who prefer to use the command line.
This document serves as a reference for operating rodo. This document assumes you have basic command line skills.
If you are experienced in setting up software projects, you can skip to the Quick start section.
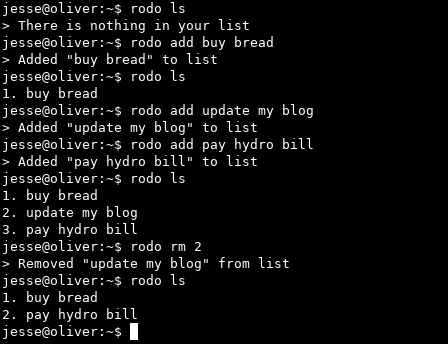
Screenshot
Table of Contents
- Quick start
- Conventions used in this readme
- Platforms
- Requirements
- Getting started
- Using rodo
- List of commands
- Usage examples
Quick start
Note - This section is for users who are familiar with git, a Unix-like command line environment, or scripting.
- Make sure Racket is installed
git clone https://github.com/m455/rodocd rodosudo ./install.shrodo
Note: To uninstall, run sudo ./uninstall.sh
Conventions used in this readme
- Note - Notes signify additional information
- Tip - Tips signify an alternate procedure for completing a step
- Caution - Cautions signify that damage may occur
- Example - Examples provide a visual reference of how a procedure would be carried out in the real world
Inline code- Inline code signifies package names, filenames, or commandsCode block- Code blocks signify file contents
Platforms
Below is a list of platforms that rodo can run on:
- GNU/Linux
- Windows Subsystem for Linux
- macOS (Untested)
Requirements
The following items must be downloaded and installed before you can use rodo:
- Racket: https://racket-lang.org/
- rodo's source code: https://github.com/m455/rodo
Downloading Racket
The Racket programming language will be needed to create a single-file executable
To download and install Racket
- Run
sudo apt install racketon the command line
Downloading the rodo source code
rodo's source code is needed so Racket's raco tool can create a single-file executable
To download the rodo source code
- Run
git clone https://github.com/m455/rodo
Getting started
This section will guide you through settig up rodo.
Note: This section assumes you have already downloaded the rodo source code.
Installing rodo
Installing rodo will add a rodo executable to the /usr/local/bin directory. This allows users to
run rodo from any directory on their system.
Note: Writing to the /usr/local/bin directory requires root privileges.
To install rodo
- Change to the directory you downloaded rodo into
- Run
sudo ./install.sh
Uninstalling rodo
Uninstalling rodo removes the rodo executable from the /usr/local/bin directory.
To uninstall rodo
- Change to the directory you downloaded rodo into
- Run
sudo ./uninstall
Using rodo
This section will teach you how to use rodo's commands.
Note: This section assumes you have installed rodo.
Showing the help message
The help message will provide a list of available commands. This is list useful in case you forget the name of a command or how to use a command.
To show the help message
- Run
rodo -h
Initializing rodo
Before using rodo, you must initialize rodo. Initializing will allow you to save your list to a text file for later access.
To initialize rodo
- Run
rodo init
Displaying your list
Displaying your list will allow you to view items you have added to your list. You will notice numbers beside the items in your list.
Note: These numbers are useful references for when you want to remove items from your list. For more information, see the Removing an Item from Your List topic.
To display your list
- Run
rodo ls
Adding an item to your list
Adding an item to your list will save it to a text file to access later.
To add an item to your list
- Run
rodo add "this is an example of an item using double quotation marks"
Note - The double quotation marks are optional, but recommended
Removing an item from your list
When removing an item from your list, you can reference the numbers beside each item when Displaying Your List. You can use these numbers when removing an item from your list.
To remove an item from your list
- Run
rodo rm 1
Note 1 - The "1" in the procedure above will remove the first item in your list.
Note 2 - You may need to run rodo ls first to see which numbers correspond
with which item in your list.
Configuring rodo
You can configure rodo's settings, such as the location of the list file, and command names.
To configure rodo
Caution: Changing the config.rkt file should be done at your own risk as it may break rodo's functionality
- Edit the
config.rktfile
List of commands
This section lists and describes rodo's commands.
-hor--helpdisplays the help messageinitcreates a list file (See theconfig.rktfile for the default location of this file)lsdisplays your listaddadds an item to your listrmremoves an item from your list
Usage examples
The examples below assume that you have added rodo to your $PATH.
rodo -h
rodo --help
rodo init
rodo ls
rodo add "this is an item"
rodo add this is an item without quotation marks
rodo rm 1
Note: You may have to run rodo ls to see which number corresponds to which item in your list.